11 BASIC THINGS YOU MUST KNOW ABOUT IP ADDRESSES
As you probably already know, all devices connected to the internet have their unique IP address. However, there is a lot more to that you might not be aware of.
In this article you will read about all the basic FAQs regarding IP addresses that might have crossed your mind.

Table of Contents
What are the types of IP addresses?. 1
Shared and Dedicated IP address. 2
What are the different versions of IP addresses?. 2
What is Domain Name System?. 3
What is the process for allocating IP addresses?. 3
What is subnetting, and how does it work?. 3
How to find your IP address?. 4
How to hide your IP address?. 4
Does your IP address change?. 4
What is blacklisting and whitelisting IP addresses?. 5
What is an IP address?
The “IP” in an IP address refers to the Internet Protocol. The “address” element refers to a unique number. This number associates with all of your online activities. It is very similar to the return address on a letter.
IP addresses are sets of numbers issued to computers, routers, websites and many more. It functions similarly to a conventional address. They pinpoint the location of every device or system in the network anywhere on the planet. The TCP/IP Protocol uses them to let devices communicate among themselves.

A domain URL conceals the string of digits on genuine websites. This makes it easier for consumers to remember.
How does IP address work?
Information transmits across the network in discrete pieces called packets. Each packet contains the data the sender is trying to communicate. It also includes a header containing metadata about that packet.
The packet header contains the IP addresses of transmitter and receiver devices. Routers and other network infrastructure use this information. They ensure that packets get to where their appropriate destination.
What are the types of IP addresses?
There a many different types of IP address. Namely, they are:
· Dynamic
· Static
· Public
· Private
· Shared
· Dedicated
· Loopback
Dynamic IP address
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) allocates dynamic IP addresses. These addresses are on lease and change on a regular basis. Home routers and small networks, all use dynamic IP addresses. Simply told, it’s the default setting offered by most Internet Service Providers.
Static IP address
Static IP addresses do not change after their allocation. Until the network equipment’s decommission, they will remain the same. The ISP assigns this form of IP address, which can be more expensive than a typical dynamic address. They usually refer to servers and other major network systems. They can also correspond to specific devices. However, proper configuration and support of security standards is essential. Lack of these might provide security concerns.

To get a static IP address for your devices, contact your Internet Service Provider. You can inquire about the choices they provide as a service. To keep your static IP address safe, you will need a lot of technical knowledge.
Public IP address
Public IP address is often popular as External IP address. This is the address that a router or network uses for external communications. External communication refers to interactions outside its own network. A service like What Is My IP Address displays your public address. Only one router or network at a time can utilize a public address. If the IP is dynamic, another router may use it after the lease expires.
Private IP address
All devices in a network get their own private IP address, often known as Local or Internal. This set of numbers assigns to each device that connects to a network. It is in the order in which it connects to the router or server within any network. A router will have a public IP address as well as a private address. The private address of all routers from that manufacturer will be same anywhere in the globe. Routers from Linksys utilize 192.168.1.1. Others like D-Link and NETGEAR use 192.168.0.1.
Shared and Dedicated IP address
The terms “shared” and “dedicated” are usually in use in the context of internet domains. Every website has an IP address. Even with different domains, sometimes a number of distinct websites might share them. Only one website can use a dedicated IP address.
Dedicated hosting frequently includes a dedicated IP address. It reveals the address to the other websites on the server in the event of shared hosting. Even if you’re utilizing a shared host, you can request a dedicated address.
If you want to learn more about having a dedicated IP address for your website, research about your host’s options.
What are the different versions of IP addresses?
IP addresses are categorically of two kinds: IPv4 and IPv6. Each has its own format. The main distinction between the two is that the latter can exist in far greater numbers than the former. (2128 and 232 respectively)
IPv4
You can split IPv4 addresses into 4 pieces. Dots separate each part, as follows:
45.48.241.198 is the IP address of a server located in the United States.
Each of these four integers is in normal decimal notation. Computers work with binary numbers. Each of them corresponds to an eight-bit binary value ranging from 0 to 255. This means that none of them can be more than 255 (111111 in binary).
IPv6
IPv6 is a newer version of the protocol. It is gradually overtaking IPv4, and its addressing is as follows:
2620:cc:8000:1c82:544c:cc2e:f2fa:5a9b
Here, there are eight numbers instead of four. Colons divide each section of the address. IPv6 addresses feature numbers in hexadecimal (Base 16) notation.
The difference between the 8-bit components of IPv4 and 16-bit components of an IPv6 is noteworthy. This is a major reason for IPv6’s existence.
IPv4 addresses are of 32 bits. Therefore, the number of possible unique IPv4 addresses is a little less than 4.3 billion. That amount looked adequate in the early days of the internet. However, the number of internet-connected devices grew over time. This, then began to emerge as a potential crisis. IPv6 addresses have a 128-bit length. Hence, the number of unique IPv6 addresses is a lot higher. (340 undecillion)
What is Domain Name System?
This is how matching of domain names and IP addresses take place.
Most internet-connected devices also have human-readable addresses called domain names. The Domain Name System, or DNS, is another component of the Internet protocol. It ensures that domain-name requests get to the correct IP address. In addition to the IP-address architecture, DNS works as a more user-friendly layer.

However, IP address is still the most common way to locate internet-connected gadgets. Especially since a domain name might sometimes correlate to many servers. This means they will point to various IP addresses.
What is the process for allocating IP addresses?
International Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) describes the allocation of IP addresses. Both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses are normally given in a hierarchical manner. The IANA assigns IP address blocks to regional internet registries. Here, you can check which address ranges hail from which areas. Regional registries then assign smaller blocks to national registries and so on. This process continues until individual ISPs receive the blocks. ISPs give specific IP address to an individual device.
What is subnetting, and how does it work?
Businesses get IP address ranges based on the number of networks and hosts that they may require. The Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) assignment technique is now popular for such allocations.
Organizations use subnetting divides the given address space into smaller allocations. These allocations correspond to each subnetwork inside the organization. Subnetting increases the number of subnetworks. And it decreases the number of viable host IP addresses. Each of these subnetworks is an IP subnet.
Subnetting and route summarization help to reduce the size of routing tables. This makes routers more efficient. Routers far from a destination do not require a lot of addressing information. This helps in simplifying routes to a considerable extent. As packets approach the target network, they need more local routing information. One such example is the local subnet mask. Routers can discern which specific network segment includes the destination host. It can then deliver the packet properly by applying the mask to the its destination address.
How to find your IP address?
You might be wondering what the IP address of your networked device is. There are several websites that will tell you that. One such website is whatismyipaddress.com. This is quite simple. Every network packet you send out to the internet has that information.
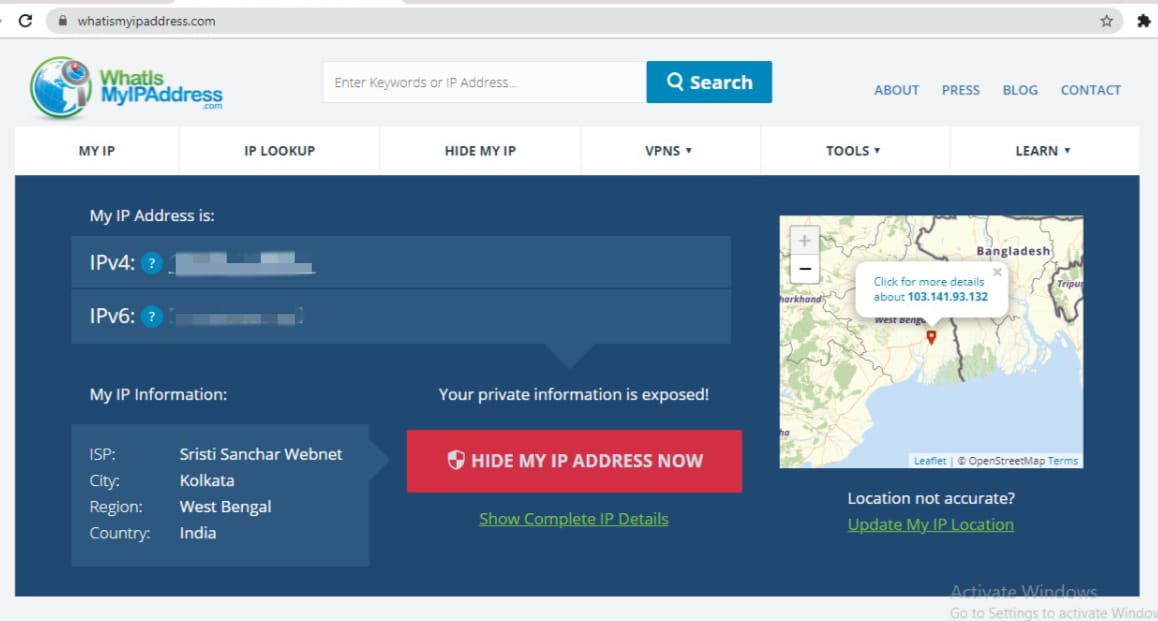
Majority of people connect their devices to a local network. In this case, the result you will obtain is the public-facing IP address set to your router. You will need to go into your device’s network settings to get your private IP address on your local network. Lifehacker sets down the procedures you’ll need to take.
How to hide your IP address?
Your IP address contains a lot of information about you. This includes your estimated geographic location and other private information. So, you may want to conceal it for a variety of reasons. Using a virtual private network (VPN) is one technique to do so. A VPN service can create an encrypted tunnel from your device. it will connect to the VPN provider’s private network via the public internet. It is similar to connecting to your home network, only the router could be halfway across the globe. To external websites, the IP address of the VPN host will appear to be your IP address. IP addresses do not provide much privacy but VPNs provide a clever solution to bypass this.

Both devices must have suitable VPN software. One can built VPN tunnels from the originating device to the destination device. Many businesses have VPN gateways that allow them to construct such tunnels. They run between themselves and remote devices with compatible VPN software.
If your country has a website blocked within its territory, you can use VPNs to access it. It will also let you access a version of a website hosted in another country.
Does your IP address change?
Yes, your IP address can change for a variety of reasons.
If you turn your modem or router on and off, it can alter. Alternatively, you can contact your Internet service provider. You can then have them make the necessary changes.
Furthermore, if you go on vacation with your laptop, your home IP address does not accompany you. It can’t since you will be connecting to the Internet over a different network. The IP address will keep changing as you travel from the airport to the hotel. This will go on if you use the public internet of those places.
When you connect to a Wi-Fi in a new city or anywhere outside, you are using a separate and temporary IP address. The ISP of that Wi-Fi assigns the IP address to your device.
What is blacklisting and whitelisting IP addresses?
You can blacklist or whitelist IP addresses for security reasons. These security measures protect your website and dashboards from spammers’ and hackers’ threats.
When you blacklist an IP address, it prevents them from accessing your website.
The opposite of blacklisting is whitelisting. You choose to grant permission to some specific IP addresses only. This bans all other IP addresses when you whitelist.
If you have been curious about IP addresses and how they function, we hope this article has given you a better understanding of the subject.